2.2.3 Sound Levels
It is important to understand what sound levels are acceptable in a given space. Excessive background noise can originate within or outside a space and impact inhabitants in a myriad of ways ranging from annoyance and distraction to aggressive behaviour and hearing impairment. Sound level is measured in sound pressure (decibels (dB)) at different frequency levels (Hertz (Hz)).
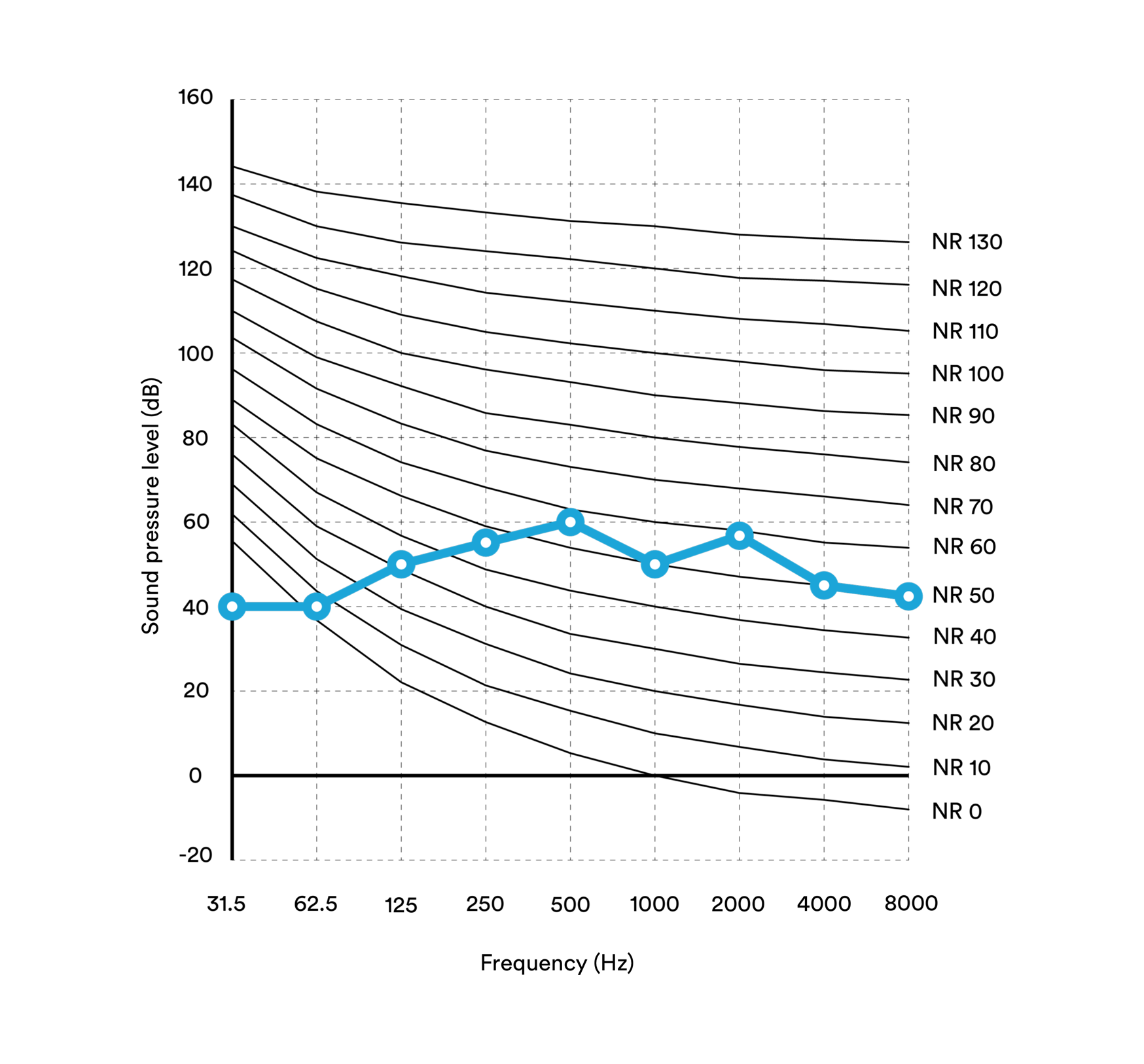
The International Organization for Standardisation (ISO 1973), the American National Standards Institute (ANSI 1995), and other international organisations, set standards for acceptable sound levels in indoor environments to preserve hearing, clear speech communication and minimise annoyance. The ISO Noise rating (NR) curves, for example, indicate the maximum allowable sound pressure level at different frequencies, varying according to different types of spaces and their intended use. Each maximum rating level is indicated by a NR value.
To determine a NR value for a given space, the sound frequency spectrum of the noise in an unoccupied room is measured. The obtained spectrum of values are then plotted on a graph and compared against the noise rating curves to determine a rating (see calculation example).
Speech intelligibility is calculated according to a standard index using acoustical measurements of speech and noise. A number of factors influence speech intelligibility, including ambient noise level, reverberation time, the frequency response of a room, psychoacoustic masking effects, as well as the quality of any sound reproduction equipment being used to transmit sound in the space.
The Speech intelligibility index (SII) is represented on a numeric scale called the Common Intelligibility Scale (CIS). The value ranges from 0 to 1, or bad to excellent, and indicates the degree to which a space, aka transmission channel, degrades speech intelligibility).
| Maximum Noise Rating Level | Applications |
|---|---|
| NR 25 | Concert halls, broadcasting and recording studios, churches |
| NR 30 | Private dwellings, hospitals, theaters, cinemas, conference rooms |
| NR 35 | Libraries, museums, court rooms, schools, hospitals, operating theaters and wards, flats, hotels, executive offices |
| NR 40 | Halls, corridors, cloakrooms, restaurants, night clubs, offices, shops |
| NR 45 | Department stores, supermarkets, canteens, general offices |
| NR 50 | Typing pools, offices with business machines |
| NR 60 | Light engineering works |
| NR 70 | Foundries, heavy engineering works |
Previous Chapter Next Chapter
Download The Book of Acoustics